Physics (17/17)
1. start physics
Make sure to activate the physics engine before using physics blocks. (Or no physics block is working!)
Once the engine is enabled, the stage seems to have gravity as the sprite has gravity, mass, friction, ect.
Application: this block can be used to create games like Super Mario Bros.
2. stop physics
- Once the physics engine is deactivated, all physics effects of the sprite will disappear.
3. [with] collision
Set whether the sprite will collide with other sprites or not.
If the sprite does not participate in a physical collision, other sprites will not have a physical collision effect when they encounter this sprite. Furthermore, Physics blocks would have no effect on this sprite, that is, no gravity, no mass, no rebound, and so on.
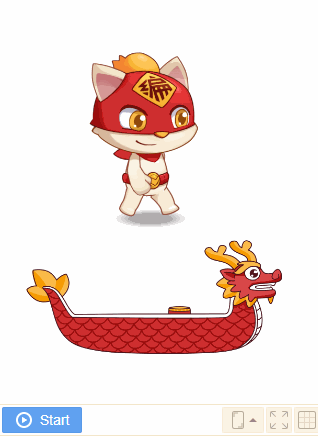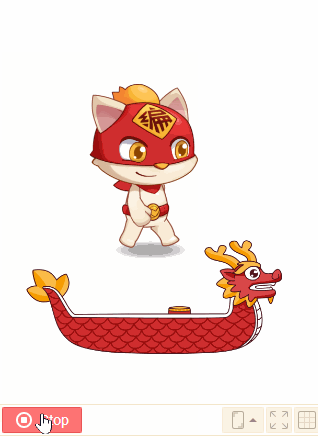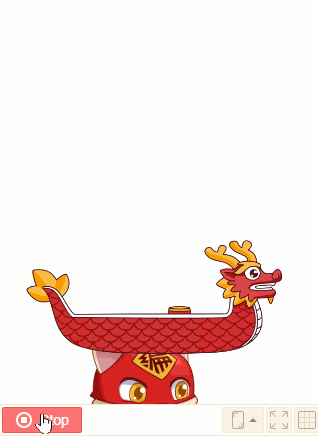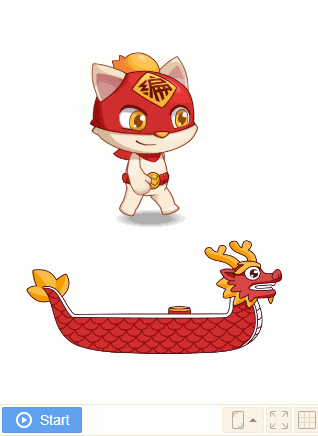
4. [enable] to fall
Falling effect will appear if the sprite is enabled to fall when it is falling. Both the shape and the mass of sprite will affect the falling effect.
Usually the larger the mass of the sprite, the more obvious the collision.
Tip: with this block, you can create games like Angry Birds.
5. set gravitational acceleration to (10) at (-90) degrees
Change the force degree and direction of the graviton acceleration.
Value range: -10000 to 10000
Force degree: the default value is 10. The greater the gravitational acceleration, the faster the velocity of the free-fall body.
Direction: the default direction is -90 degrees. When the derection is -90 degrees, the sprite falls directly down when start physics.
6. set gravitational acceleration to (10) with direction controlled by phone
Set the gravitational accerlation, whose direction can be changed by tilting the phone.
Value range: -10000 to 10000
Force degree: the default value is 10. The greater the gravitational acceleration, the faster the velocity of the free-fall body.
When tilting a mobile phone, gravity is always consistent with the direction of real gravity, that is, vertical down.
7. set physical edge as [no edge]
Set the physical edge of the stage when start physics. Collision can not happen beyond the edge.
The default style is [no edge].
4 edges are available in drop-down list.
8. set mass to \10)
The default mass of a sprite is related to its area. The larger the sprite, the greater the default mass.
This block can set sprite's mass to input value.
- Value range: 0~10000
9. set density to (1)
Set the density of the sprite, which would affect sprite's mass.
Value range: 0 to 10000
In Kitten Editor, density = mass ÷ area
10. set friction coefficient to (0.5)
The greater the friction coefficient, the greater the resistance of the sprite.
- Value range: 0 to 1. Decimal value is available.
11. set restitution coefficient to (0.9)
It is easy to achieve the rebound effect of elastic ball.
- Value range: 0 to 1
12. set sprite material as [common]
Set the sprite's material: mass, density, friction coefficient, and restitution coefficient.
- 4 materials are available now: common, iron, wood and elastic.
13. [speed] of [itself]
- Get the sprite's physical properties like speed, mass, density, friction coefficient or restitution coefficient.
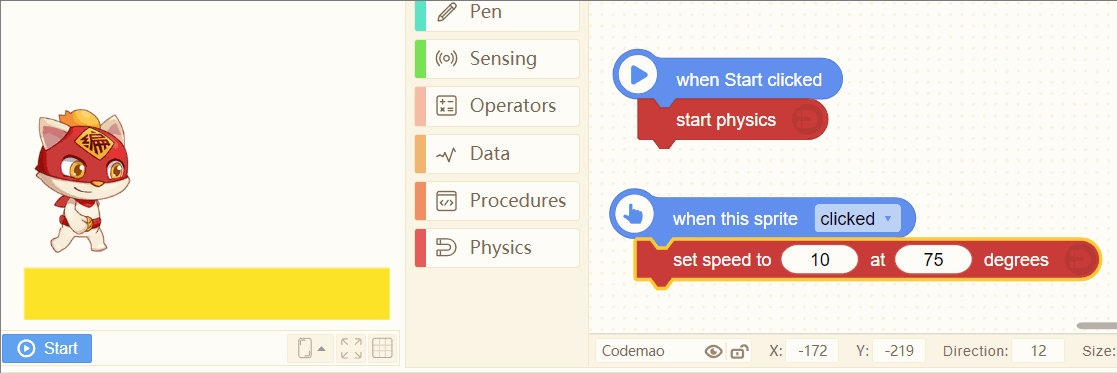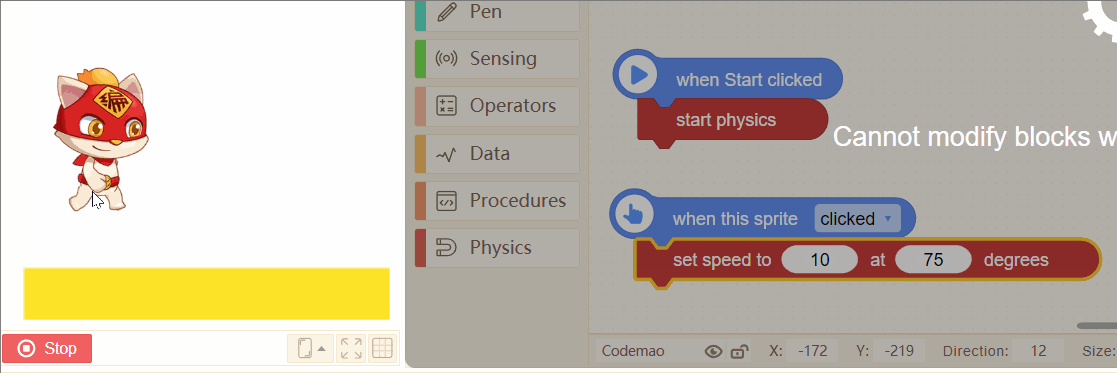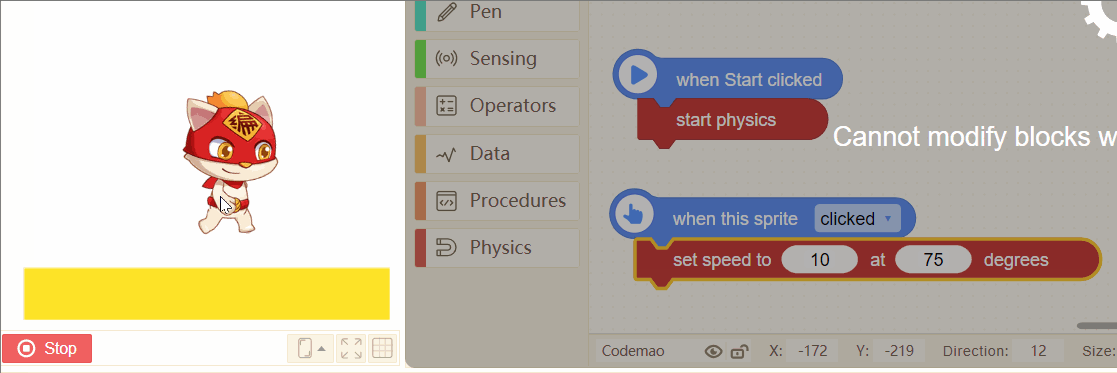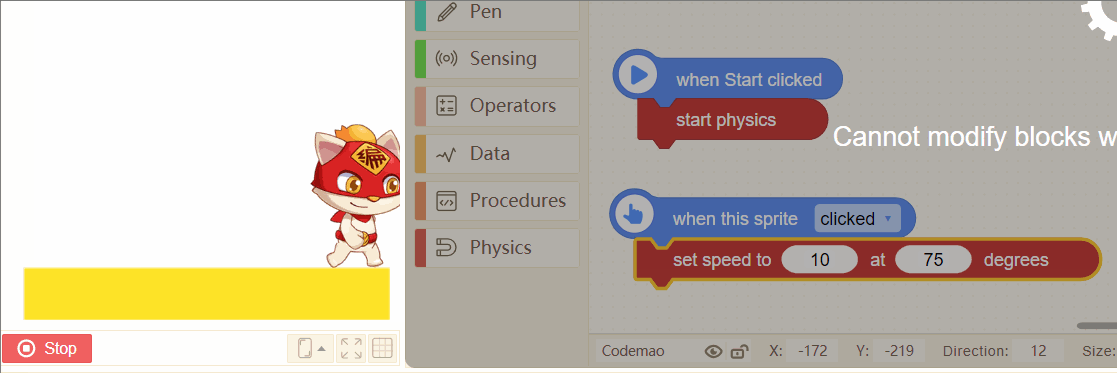
14. set speed to (5) at (0) degrees
Set the instantaneous speed of a sprite at a certain time. The speed and direction can be changed.
Tip:
If you want the achieve jumping effect of a sprite, you can try these blocks.
Set a proper speed, and direction from 45 degrees to 75 degrees is better~
15. set speed at X-axis to (5), Y-axis to (5)
Input the speed at X-axis and Y-axis to set the instantaneous speed of a sprite at a certain time.
It can determine the direction and speed of the sprite's movement.
16. set force to (5) at (0) degrees
- Set the force of a sprite at a certain time
17. set force at X-axis to (5), Y-axis to (5)
- Input the force at X-axis and Y-axis to set the sprite's state of stress at a certain time
- Physics (17/17)
- 1. start physics
- 2. stop physics
- 3. [with] collision
- 4. [enable] to fall
- 5. set gravitational acceleration to \(10\) at \(-90\) degrees
- 6. set gravitational acceleration to \(10\) with direction controlled by phone
- 7. set physical edge as [no edge]
- 8. set mass to \10\)
- 9. set density to \(1\)
- 10. set friction coefficient to \(0.5\)
- 11. set restitution coefficient to \(0.9\)
- 12. set sprite material as [common]
- 13. [speed] of [itself]
- 14. set speed to \(5\) at \(0\) degrees
- 15. set speed at X-axis to \(5\), Y-axis to \(5\)
- 16. set force to \(5\) at \(0\) degrees
- 17. set force at X-axis to \(5\), Y-axis to \(5\)